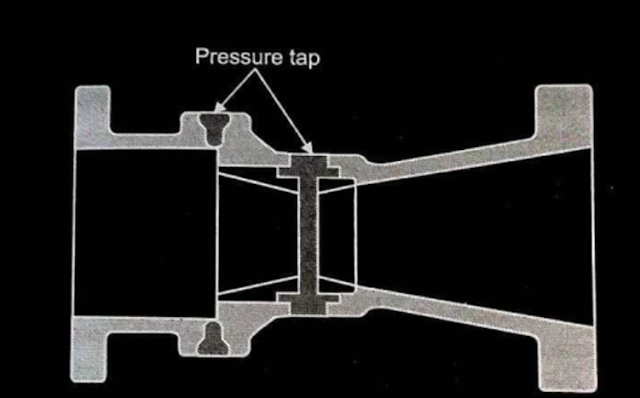
Construction
It is a type of flow meter that is a combination of a Venturi tube and an orifice plate.
It has a higher ratio of pressure developed to pressure lost than a Venturi tube, but a lower ratio than an orifice plate.
It is more compact than a Venturi tube, but requires more straight pipe upstream and downstream than an orifice plate.
It is typically used for large flow rates.
It has a lower permanent pressure loss than a Venturi tube.
It is not as sensitive to upstream disturbances as an orifice plate.
The main components of a Dall tube are:
Inlet shoulder: This is a short, straight section of pipe that precedes the converging cone.
Converging cone: This is a section of pipe that gradually decreases in diameter.
Throat: This is the smallest section of pipe in the Dall tube.
Diverging cone: This is a section of pipe that gradually increases in diameter after the throat.
Slotted annulus: This is a narrow gap between the converging and diverging cones.
Pressure taps: These are ports that are used to measure the pressure drop across the Dall tube.
The Dall tube works by measuring the pressure drop across the throat. The pressure drop is proportional to the square of the flow rate, so by measuring the pressure drop, the flow rate can be calculated.
Dall tubes are a versatile type of flow meter that can be used in a variety of applications. They are typically used for large flow rates, but can also be used for smaller flow rates if the permanent pressure loss is acceptable.
Working:
It is another restriction type primary element for flow measurement. It is a shortened/modified form of a Venturi meter. The differential pressure of Dall tube is midway of-the orifice and venturi tube. It consists of two sections, with relativity large cone angle. The short straight inlet followed by an abrupt decrease in diameter. A narrow annular slit separates the short inlet and divergent outlet. The throat is formed by a circumstantial slit located between the inlet and outlet cones. The higher pressure is measured at circular slit area, and lower pressure is-measured at upstream. Typically a lithium coating is provided to avoid corrosion of the device by the fluids. The differential pressure produced by Dall tube is much higher, nearly doubled to that of Venturi meter having the same upstream and throat, diameters with the same net head loss. ,It. causes a very low-pressure loss compared to other differential pressure flow elements. Up to '95% Differential pressure can be recovered.
Advantages:
Low permanent pressure loss
Less maintenance and inspection required
Short length
Wear and erosion are negligible
Available in numerous materials of construction
Disadvantages:
Requires a longer straight pipe upstream of the meter
Sensitive to upstream disturbances
Not suitable for hot feed water
Not suitable for fluids with suspended solids
Applications:
i) Applicable to where a significant pressure drop is not
tolerated. For example: Gas transmission pipeline