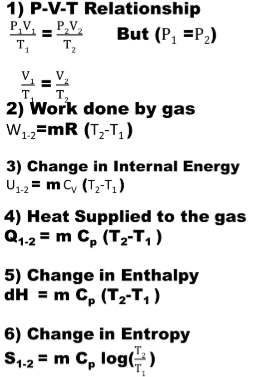Ideal Gases and Ideal Gas Processes
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas or a hypothetical gas composed of a set of randomly moving,
Non-interacting points are like particles and they always obey the gas law.
come on
An ideal gas can be defined as a state of matter whose vaporization is complete and which strictly obeys the gas laws under all conditions of pressure and temperature .
Assumptions for Ideal Gas
1) An ideal gas contains a large number of
same molecule
2) Molecular size is negligible.
3) have molecular speeds and directions
distributed randomly
4) there is no attractive force between
molecule.
5) All collisions are perfectly elastic and
temporary.
gas law
The behavior of a gas undergoing any change is studied with respect to its pressure, temperature and volume.
according to their behavior it is governed by the observance
Three Laws:
1] Boyle's law
2] Gay -Lussac's law
3] Charles's law
Boyle's law
Boyle's law states that " the absolute pressure of a given mass of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume, when the temperature is constant".
charlie's law
Charles's law states that, "The volume of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature when the pressure is constant."
Gay-Lussac's law states that, "The absolute pressure of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature, when the volume is constant."
Joule's law states that, "The change in internal energy is directly proportional to the change in temperature."
various gas processes
Various gas processes are listed
Down:
1) isobaric process
2) isochoric process
3) isothermal process
4) isentropic process
5) Polytropic process
isobaric process
If the pressure of the gas remains constant during the process then the process is called isobaric or constant pressure process.
2) isochoric process
If the volume of a gas remains constant during a process, the process is said to be a process or isochoric constant volume process.
3) isothermal process
If the temperature of the gas remains constant during expansion or compression then the process is called isothermal process or constant temperature process.
When the working substance in a system neither receives nor gives out heat to the surrounding during compression or expansion the process is called as isentropic process or Adiabatic process.
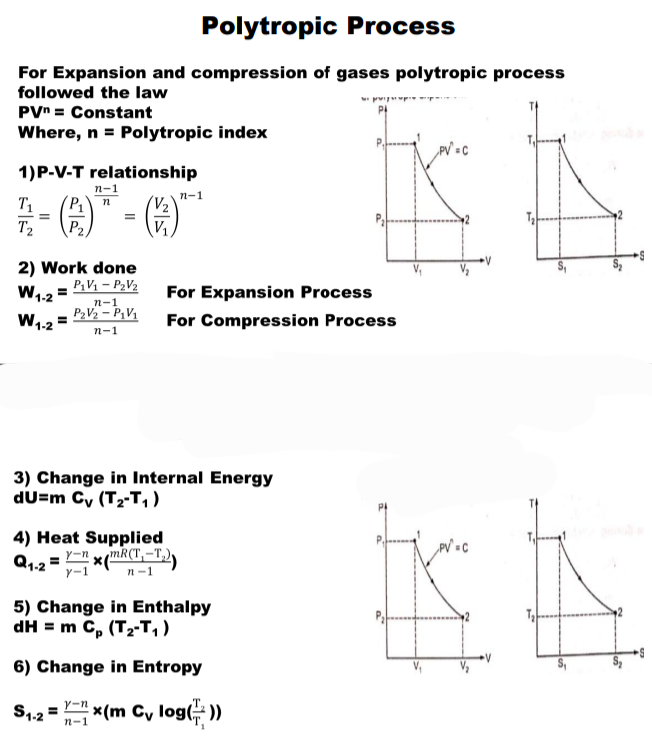
For Expansion and compression of gases polytropic process followed the law
P * V ^ n = 4 Constant